Angular momentum can be tricky to grasp. Whether you are entirely new to the concept or just need a quick refresher, look no further! We here at Out-Class have prepared a handy revision guide for the angular momentum formula below.
Why is Angular Momentum Important in Chemistry?
In Chemistry, one of the first things we learn is the atomic model. We know that electrons move in specific orbitals around an atom's nucleus. But to describe this circular motion of electrons, we need a quantity called angular momentum.
Whereas linear momentum p = mv is about straight-line motion, angular momentum is about spinning or rotating motion, such as that of electrons around a nucleus!
What is the Angular Momentum Formula?
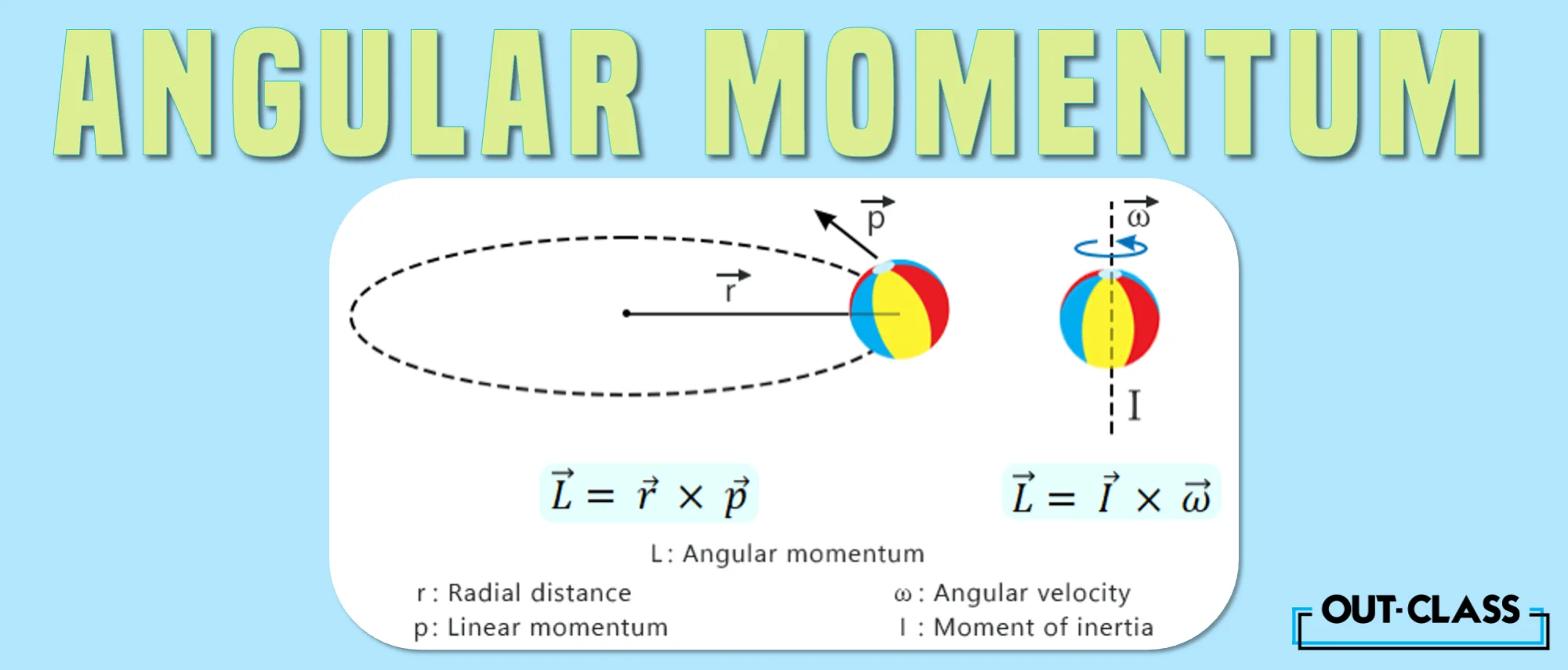
The angular momentum formula vector is given by:
L = r p
Where:
-
r = radius vector
-
p = linear momentum vector
As you can observe, the angular momentum vector is just the cross-product between the radius and the linear momentum. Hence, it can also be written more simply as:
L = mvr
Where:
-
m = mass
-
v = velocity
-
r = radius
Unit of Angular Momentum
The SI unit and dimension of angular momentum are important to understand.
The SI unit of angular momentum is:
kg m2 s-1
To arrive at these SI units, we just had to multiply the SI units of each component in the formula of angular momentum, L = mvr, as follows:
-
m kg
-
v m s-1
-
r m
The dimension of angular momentum is:
[M] [L] 2 [T] - 1
Conclusion
In short, understanding the angular momentum formula in Chemistry helps us figure out how electrons behave in atoms. Its formula is L = mvr and its SI units are kg m2 s-1.
FAQs
Q. Why is angular momentum important in Chemistry?
Angular momentum is crucial for describing the circular motion of electrons around an atom's nucleus, a fundamental concept in the atomic model.
Q. How does angular momentum differ from linear momentum?
While linear momentum is associated with straight-line motion (p = mv), angular momentum pertains to spinning or rotating motion.
Q. Can the angular momentum formula be simplified?
Yes, the angular momentum formula can be simplified as , where is mass, is velocity, and is radius.
Q. What are the SI units of angular momentum?
The SI units of angular momentum are kg m2 s−1, derived by multiplying the SI units of mass, velocity, and radius.
Q. Why is understanding the SI unit and dimension of angular momentum important?
Understanding these aspects is crucial for performing calculations and expressing angular momentum consistently in scientific contexts.