In the bustling metropolis of the cell, RNA Polymerase is the master decoder, transcribing DNA into life's instruction manual, mRNA. Let's unveil what the role of RNA Polymerase is in decoding life's code.
What is the Role of RNA Polymerase?
RNA Polymerase, often shortened to RNAP, is an enzyme responsible for transcribing DNA into RNA, a crucial step in gene expression. The primary function of RNA Polymerase is to read the genetic code in DNA and synthesize a complementary RNA strand. In essence, the RNA Polymerase function is converting the genetic information stored in DNA into a format that the cell can use, particularly in the transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA).
What is the Function of RNA Polymerase in the process of Transcription?
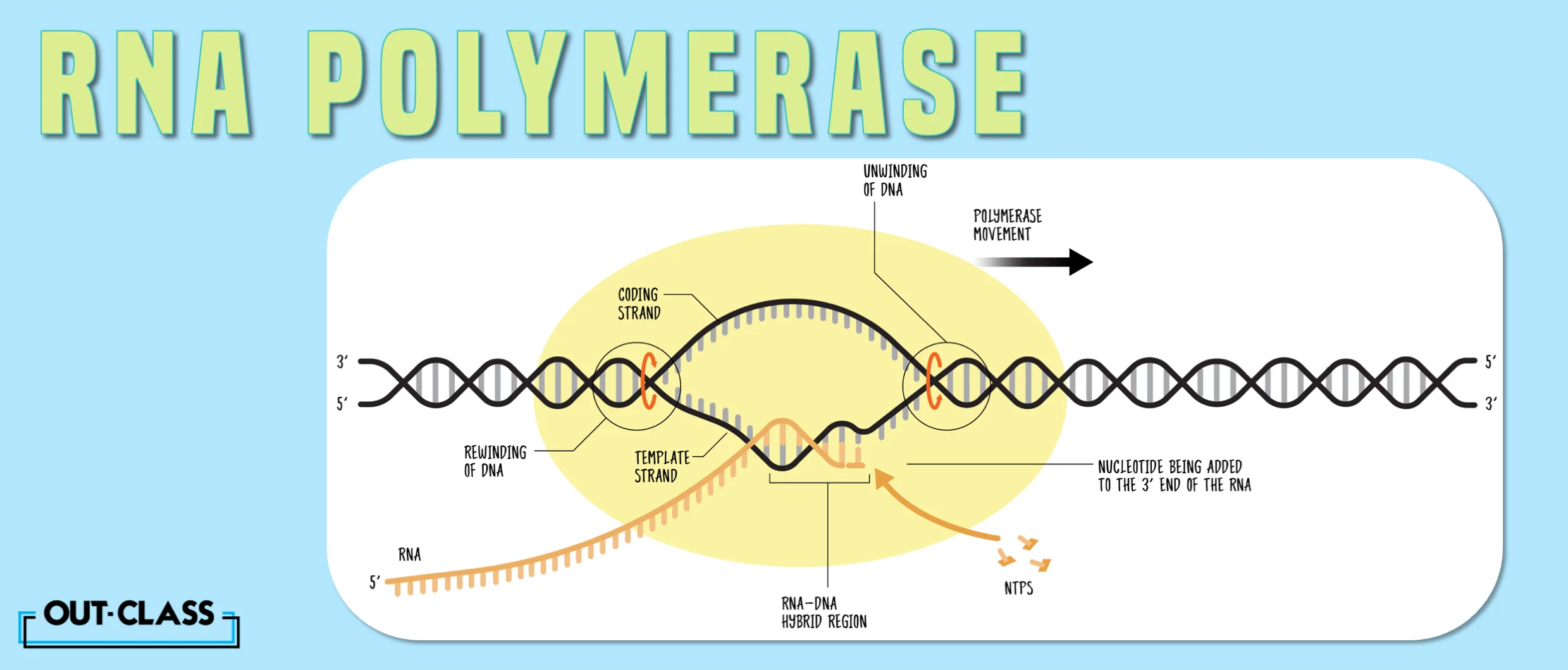
The primary role of RNA Polymerase in the transcription process is to unwind the DNA double helix and create an RNA copy, using one of the DNA strands as a template.
Stages of Transcription:
- It initiates the process by binding to a specific region of the DNA called the promoter.
- Once attached, RNA Polymerase reads the DNA template.
- It assembles RNA nucleotides to create a complementary RNA strand called messenger RNA (mRNA).
- This mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
What Does RNA Polymerase Do?
RNA Polymerase ensures that the correct sequence of nucleotides is synthesized in the RNA molecule, making it an essential component in accurately transmitting genetic information. This process is crucial for producing proteins and other RNA molecules that perform various cellular functions.
What is the role of RNA Polymerase in Transcription?
The role of RNA Polymerase in transcription involves transcribing different types of RNA, including:
- messenger RNA (mRNA)
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- transfer RNA (tRNA)
Each RNA type serves a specific purpose in protein synthesis and cellular activities in eukaryotic cells.
DNA Polymerase vs. RNA Polymerase
It's important to note that RNA Polymerase and DNA Polymerase are distinct enzymes with different functions. While RNA Polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA, DNA Polymerase replicates DNA during DNA replication. Understanding these differences is crucial to appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular processes.
Wrapping up
In conclusion, the role of RNA Polymerase in transcription is pivotal for gene expression, as it enables the translation of genetic information from mRNA to proteins. By understanding the purpose of RNA Polymerase, we're one step closer to decoding life's blueprint. We hope this study guide helped you answer 'What is the role of RNA Polymerase?'.
FAQs
Q. What is RNA Polymerase, and what is its role in the cell?
RNA Polymerase is an enzyme responsible for transcribing DNA into RNA. Its role involves decoding the genetic information stored in DNA and synthesizing RNA strands, including messenger RNA (mRNA).
Q. How does RNA Polymerase initiate the transcription process?
RNA Polymerase initiates transcription by binding to a specific region of DNA called the promoter. Once attached, it reads the DNA template and assembles RNA nucleotides to create a complementary RNA strand.
Q. What is the significance of RNA Polymerase in gene expression?
RNA Polymerase plays a crucial role in gene expression by transcribing DNA into various types of RNA, including mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. This process is essential for protein synthesis and other cellular activities.
Q. Can you explain the difference between RNA Polymerase and DNA Polymerase?
RNA Polymerase and DNA Polymerase are distinct enzymes. RNA Polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA during gene expression, while DNA Polymerase replicates DNA during DNA replication.